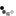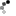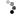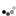 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...| Hobby Master 1:48 HA7753 P-51D Mustang - USAAF 361st FG, 375th FS, #44-13926, RAF Bottisham, England, July 1944 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale: 1:48 |
Length: 8" |
Width: 9.25" |
Composition: Diecast |
SKU: HM-HA7753 |
Period: World War II |

On July 26, 1944 P-51D Mustang #44-13926 was part of a flight of four Mustangs that was photographed from a B-17 Flying Fortress as they flew together in formation. The aircraft, three P-51Ds and one P-51B, were all from the 375th Fighter Squadron based at RAF Bottisham, England. The now famous photograph is titled "The Bottisham Four". The 375th Fighter Squadron, a component of the 361st Fighter Group, operated P-47 Thunderbolts and later P-51 Mustangs. Their missions primarily involved escorting bombers, ground attacks, and engaging enemy aircraft over Europe.
Designed to meet an RAF requirement for fighter-bomber and reconnaissance aircraft, the P-51 Mustang was first flown on October 26th, 1940. This versatile aircraft was capable of escorting bombers on long-range missions, engaging in dogfights, and dropping down to destroy German targets on the ground. At least eight versions of the P-51 were produced, but it was the definitive P-51D that gave the Mustang its classic warbird appearance. Britain and the US both tested the airframe with the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine, which gave the aircraft tremendous performance gains. The Truman Senate War Investigating Committee called the Mustang "the most aerodynamically perfect pursuit plane in existence."
Hobby Master's 1:48 scale P-51 Mustang is a well-thought-out, quality product, constructed almost entirely from diecast metal with intelligent use of plastic components. The sliding canopy opens to reveal pad printed flight controls, instrument panel and radio equipment boxes. The all-metal propeller spins freely, and the wing flaps and radiator cowling are also movable. Separately applied metal exhaust stacks have six flanged pipes on each side, and pad printed rivets can be seen on the flaps, engine cowling and rudder. Landing gear and doors are constructed as a complete subassembly for easy configuration. Releases in this series include a variety of wing mounted external fuel tanks and ordnance.
Info: P-51D Mustang - USAAF 361st FG, 375th FS, #44-13926, RAF Bottisham, England, July 1944