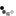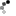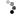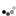 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...| TMC Models MVPP51T Nose Art Panel - P-51D "Old Crow" Bud Anderson |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale: N/A |
Length: 48" |
Width: 24" |
Composition: Diecast |
SKU: TMC-MVPP51T |
*** Aluminum Sheet (48in. x 24in) stamp with reproduction art work from the actual P-51 Mustang flown by C. E. "Bud" Anderson. ***
Clarence Emil "Bud" Anderson (born January 13, 1922) is a retired officer in the United States Air Force, a triple ace of World War II, and the highest scoring living American fighter ace. During the war he was the highest scoring flying ace in his P-51 Mustang squadron. Towards the end of Anderson's two combat tours in Europe in 1944 he was promoted to major at 22, a young age even for a highly effective officer in wartime. After the war Anderson became a well regarded fighter test pilot, and a fighter squadron and wing commander. He served his wing commander tour in combat in the Vietnam War. He retired as a full colonel in 1972, after which he worked in flight test management for McDonnell Douglas. A member of the National Aviation Hall of Fame, Anderson has remained a sought-after speaker at aviation and military events well into his 90s.
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang was an American long-range single-seat World War II fighter aircraft. Designed and built in just 117 days to a specification issued to NAA by the British Purchasing Commission, the Mustang first flew in Royal Air Force (RAF) service as a fighter-bomber and reconnaissance aircraft before conversion to a bomber escort, employed in raids over Germany, helping ensure Allied air superiority from early 1944. The P-51 was in service with Allied air forces in Europe and also saw limited service against the Japanese in the Pacific War. At the start of Korean War the Mustang was the United Nations' main fighter but the role was quickly shouldered by jet fighters, including the F-86, after which the Mustang became a specialised ground-attack fighter-bomber. In spite of being superseded by jet fighters the Mustang remained in service with some air forces until the early 1980s. As well as being economical to produce, the Mustang was a fast, well-made, and highly durable aircraft. The definitive version, the P-51D, was powered by the Packard V-1650, a two-stage two-speed supercharged version of the legendary Rolls-Royce Merlin engine, and was armed with six .50 caliber (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine guns. After World War II and the Korean War, many Mustangs were converted for civilian use, especially air racing. The Mustang's reputation was such that, in the mid-1960s, Ford Motor Company's Designer John Najjar proposed a new youth-oriented coupe automobile be named after the fighter.